Here's some basic info about the Internet
23 June 2025in the modern world, the internet has become an integral and critically important part of it, used in all areas and aspects of our lives, namely: entertainment, business, medicine, education, government administration, the military sector, banking, and others. Its main advantage is access to information, which is independent of a person's physical location. That is why it has become so popular and why it is important to have at least a general understanding of how the internet works — to avoid mistakes and fraud, especially for those who want to build a career in the field of Information Technology.
Contents
Excursion into history
In 1961, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), under the direction of the U.S. Department of Defense, embarked on a project to create an experimental data transmission network. The main objective of this network was:
Provide reliable, decentralized communication between military, governmental and scientific institutions — even in the event of a nuclear strike.
The experiment with ARPANET was so successful that many organizations wanted to join it for everyday data transmission purposes. In 1975, ARPANET transitioned from an experimental network to an operational one. The responsibility for managing the network was taken over by the Defence Communication Agency (DCA), which is now known as the Defence Information Systems Agency (DISA). However, the development of ARPANET did not stop there.
The next significant stage in development was the emergence of the World Wide Web, based on the HTTP data transfer protocol and a special format for presenting data — HTML. Until that point, the Internet had mostly been used by specialists for exchanging technical documentation and messages, primarily via email.
And the final stage in development can be considered the so-called Web 2.0 — characterized by the rapid advancement of mobile technologies. This led to a dramatic increase in data volumes, including photos and videos, as well as instant sharing of such content. The constant use of the Internet for information search marked a new era of the web. The global network became closely intertwined with satellite communications and various location-determining systems. Moreover, the low power consumption of smartphones, laptops, and other mobile devices further reduced barriers to using the Internet anytime and anywhere.
Acquaintance
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that enables real-time information exchange worldwide. It is also called a network of networks because it connects millions of local, corporate, academic, and government networks through standardized communication protocols, particularly TCP/IP.
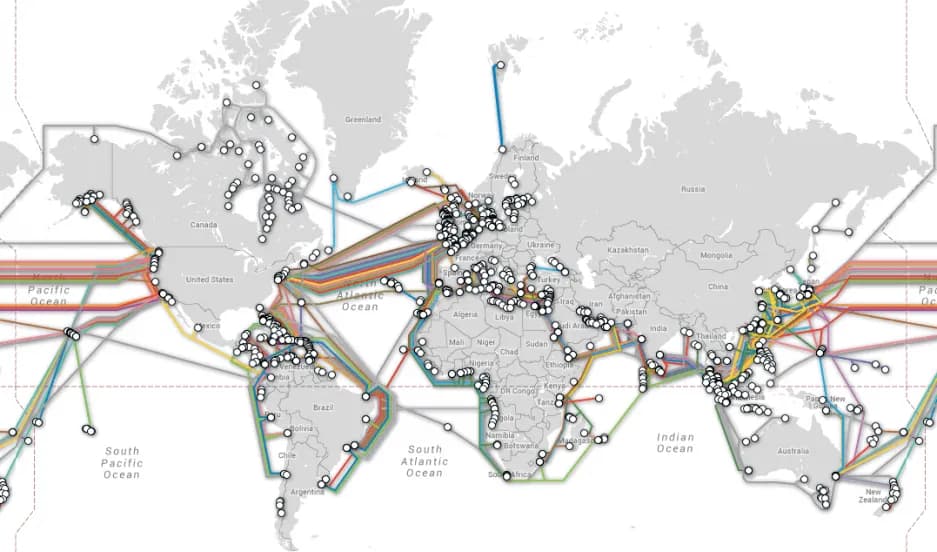
On this image, you can see what the main cable highways look like — the ones that connect all the continents and large islands together into a single network.
As of today, in 2025, major corporations in collaboration with various governments are implementing a wireless network, the essence of which is to deploy a large number of satellites into low Earth orbit. This approach aims to provide network coverage without the need to lay tens or hundreds of thousands of kilometers of cables along the ocean floor and coastal areas.

This is an approximate illustration of how it looks. Currently, their number is about 8,000, but this figure is rapidly increasing.
The Internet is actively developing toward wireless technologies because they offer several advantages, namely: the advancement of space technologies, which are harder to disable in case of war; economic benefits, as wireless requires fewer resources compared to traditional methods like cables; and an increase in the number of potential users, since many people live in hard-to-reach areas where laying cables is very difficult and economically unfeasible.
General principle of work
At a high level, the Internet works by connecting devices and computer systems together using a set of standardized protocols. These protocols define how information is exchanged between devices and ensure reliable and secure data transmission.

This diagram shows the typical way that most users send data today. But it is not the only way.
To connect to the Internet, you first need to link your computer or laptop to a router or modem — this connection is the foundation for accessing the network. When you open a browser and type in an address like “www.google.com,” your system sends a request to your Internet Service Provider (ISP), which is, in turn, connected to servers that store and process data.The browser processes the entered address and converts it into a numerical format — this is a kind of language that the system uses to recognize the unique address of a resource. The browser then sends an HTTP request to the corresponding server, which responds by sending a copy of the website in the form of small data packets.When all these packets arrive on your computer, the browser assembles them like a puzzle, and you then see the full version of the website on your screen.
The action happens so quickly that we don't even notice what's going behind. Only, when the connection is poor, you do face difficulty in reaching or loading any website or its content.
Protocols
Protocols are important for organizing communication and data transfer on the Internet. They are a set of rules and standards that govern the exchange of information between different devices and systems.
These are just the main protocols, not a complete list:
- TCP— Transmission Control Protocol is responsible for breaking down the information into parts (packets) and reassembling them correctly at the other end.
- IP— Internet Protocol defines how these packets should get from the sender to the recipient.
- LAN— Local Area Network that connects computers and other devices within a small area, such as an apartment, office or building.
- WAN— Wide Area Network іs a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographic area, such as a cities, countries and even continents.
- FTP— File Transfer Protocol protocol that allows you to transfer files between computers via the Internet or a local network.
- HTTP— Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used to transfer data between a client and a server.
- HTTPS— an encrypted version of HTTP that is used to ensure secure communication between the client and the server.
- SSL/TLS— Secure Socket Layer and Transport Layer Security protocols are used to ensure secure communications on the Internet.
- DNS— Domain Name System is responsible for converting domain names into IP addresses.
Summary
The Internet has become an integral part of modern life, providing fast access to information, communication, entertainment, learning, and work. Its operation is based on the interaction of millions of devices worldwide that exchange data according to clear rules. Thanks to this, we can find the information we need in seconds, browse websites, send messages, or work remotely. Understanding the basics of how the Internet functions helps us navigate the digital environment better and use its capabilities safely and effectively.